This page houses Debian and general Linux commands, quick little reminders for when stuff gets swapped out of my meat storage for something else. I’ve linked all the commands to relevant Unix man pages, as well as a little blurb for each one
Users and Groups
| Command | Description |
adduser <user name> |
Will run a script that asks for password, office, phone number, and other info, and creates a new user based on your answers. |
deluser <user name> |
Removes a user. |
groupadd -g <GID> <group name> |
Creates a group with the name <group name>. The -g option allows you to specify the Group ID (<GID>). The -r option creates a system group, with the allowable GIDs located in /etc/login.defs |
usermod -a -G <group(s) name> <user name> |
Add the user <user name> to the group named <group(s) name> |
groups <list of users...> |
Lists all groups each user is a member of, one user at a time. if no user(s) is specified, it lists the groups the current user is member of. |
gpasswd -d <user name> <group(s) name> |
removes the specified user from the listed groups |
id <user name> |
lists groups the specified user is a member of |
Resource Management
| Command | Description |
htop |
loads a powerful and useful task manager, with lots of configuration options, and commands to filter, kill, and adjust the nice level of a process.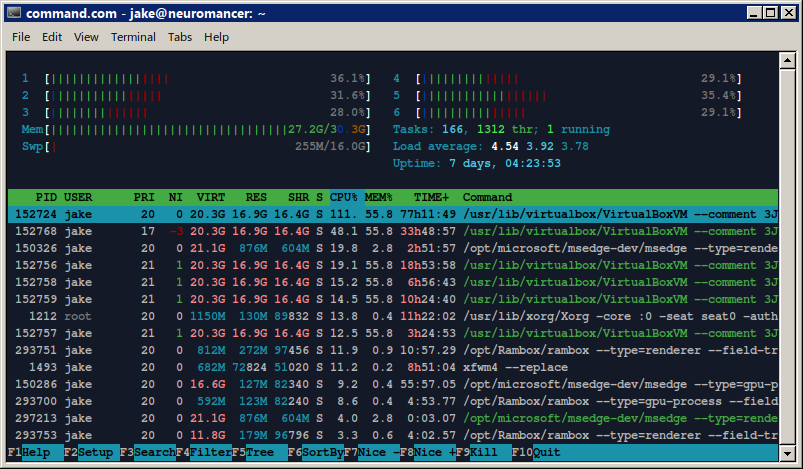 |
ls -la |
list all subdirs in a directory, with sizes and permissions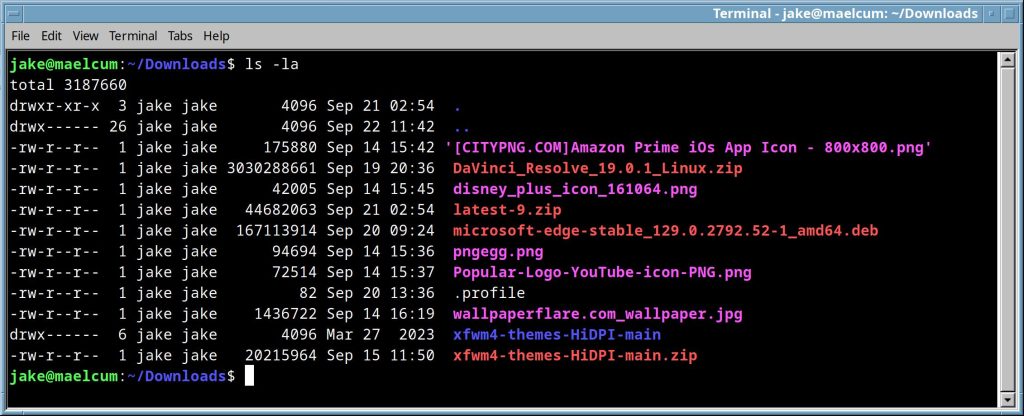 |
du -ah |
Recursively lists the child directories in the current directory, and shows disk usage in bytes for each one, and relative path.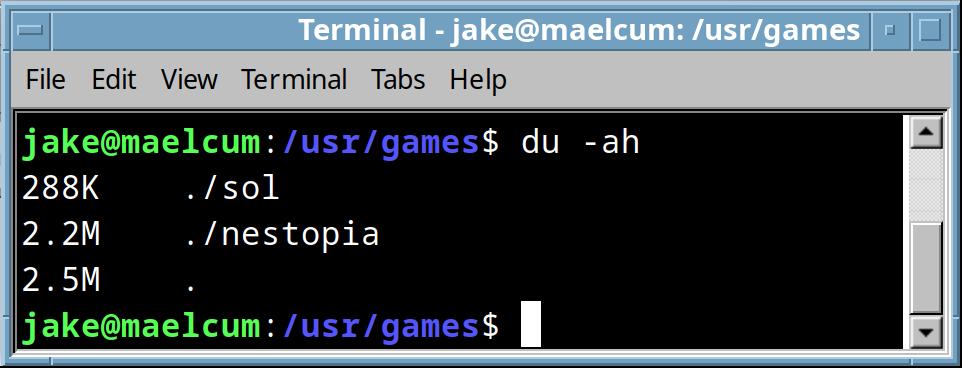 If you use the –time flag, it shows the files sorted by last modified, effectively reporting the last modified file in a directory, which can be very handy. 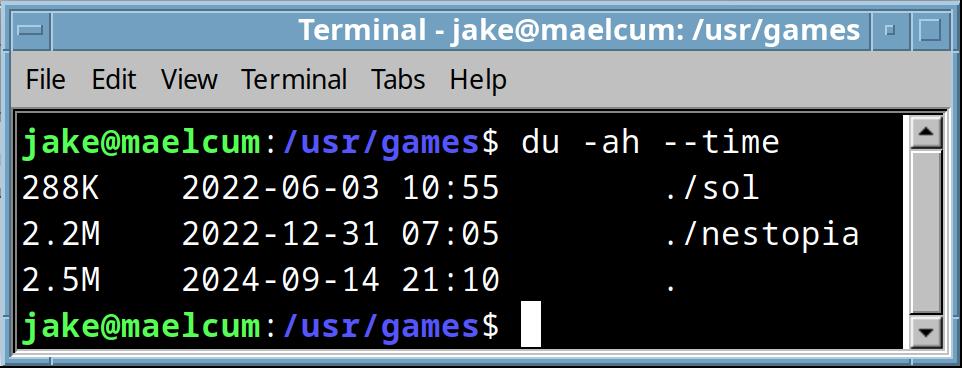 |
free -m |
Gives a report of free and used memory, with columns for shared, and buffers:
|
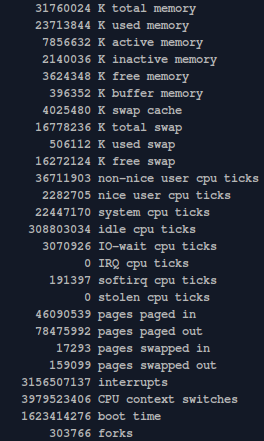
vmstat -s |
Gives a plethora of memory stats:
|
ps |
list running processes i generally use ps aux |
nice -n <integer> <process name> |
changes the nice level of a process by n amount. default is 10 |
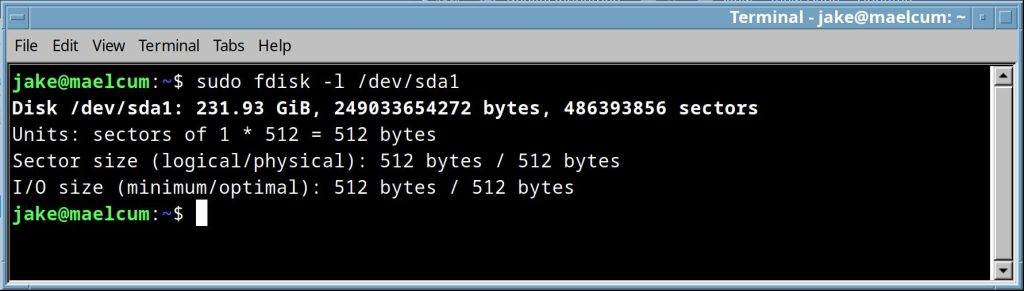
fdisk -l |
list drives and gives location on the disk, sector info and type for each partition. 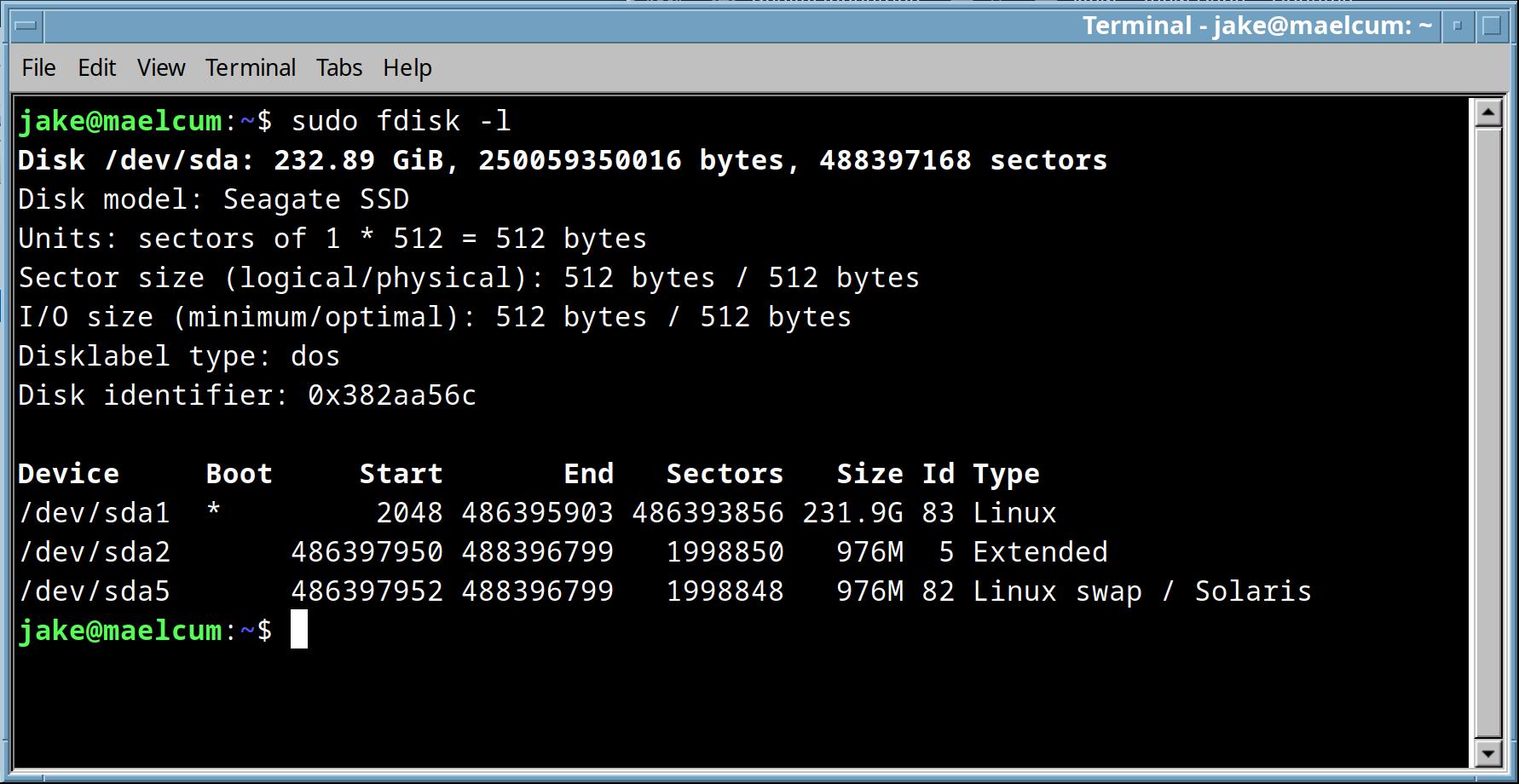
if you supply a drive name, as /dev/sda, it will give detailed info about just that drive. |
| Command | Description |
fdisk <disk> |
Opens fdisk in interactive mode, with the listed disk selected. In this state, it is like a shell, and you can add, delete, and modify partitions.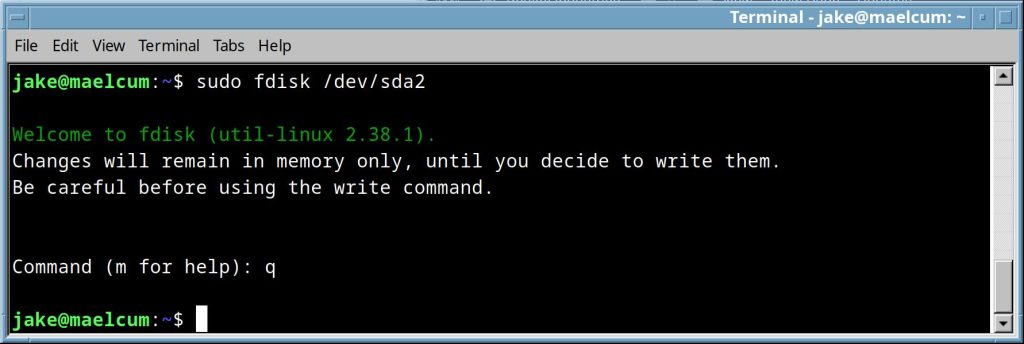 Hitting “m” will list all available commands. 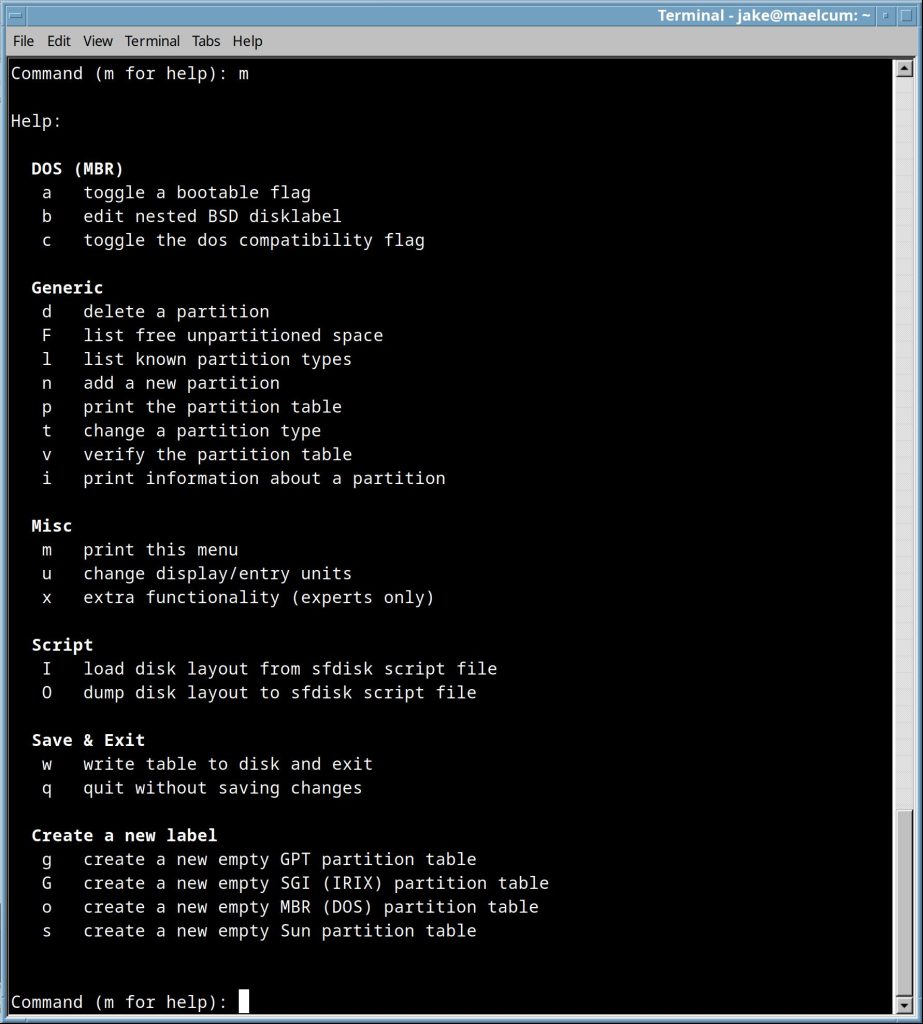 If there is a GUI present, i just use gparted. |
Service Management
| Command | Description |
systemctl <start/stop/restart/reload> <application>.service |
Performs the specified operation on the specified service. Reload will refresh the services configuration. If you don’t know if it can reload without restarting, you can use reload-or-restart |
systemctl <enable/disable> <application>.service |
Enables or disables a service. Shows exactly what it is doing, which is nice. 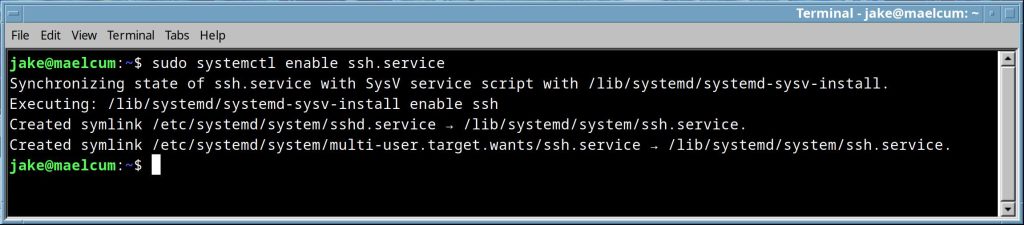 Disables a service. 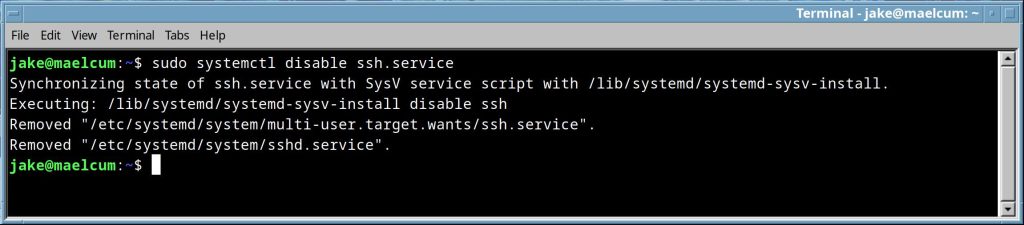 |
systemctl status <application>.service |
reports the status of a systemd service.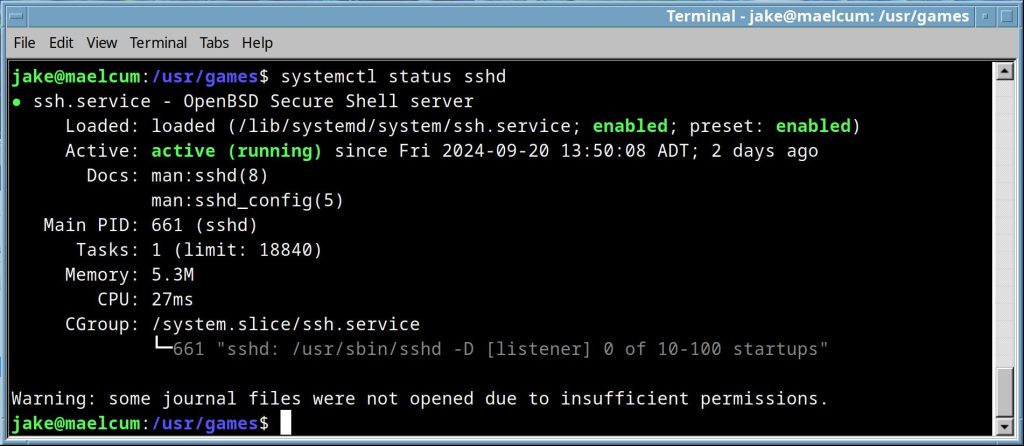 |
systemctl cat <application>.service |
Shows the Unit file of the specified service. This is the file that defines the service for Systemd.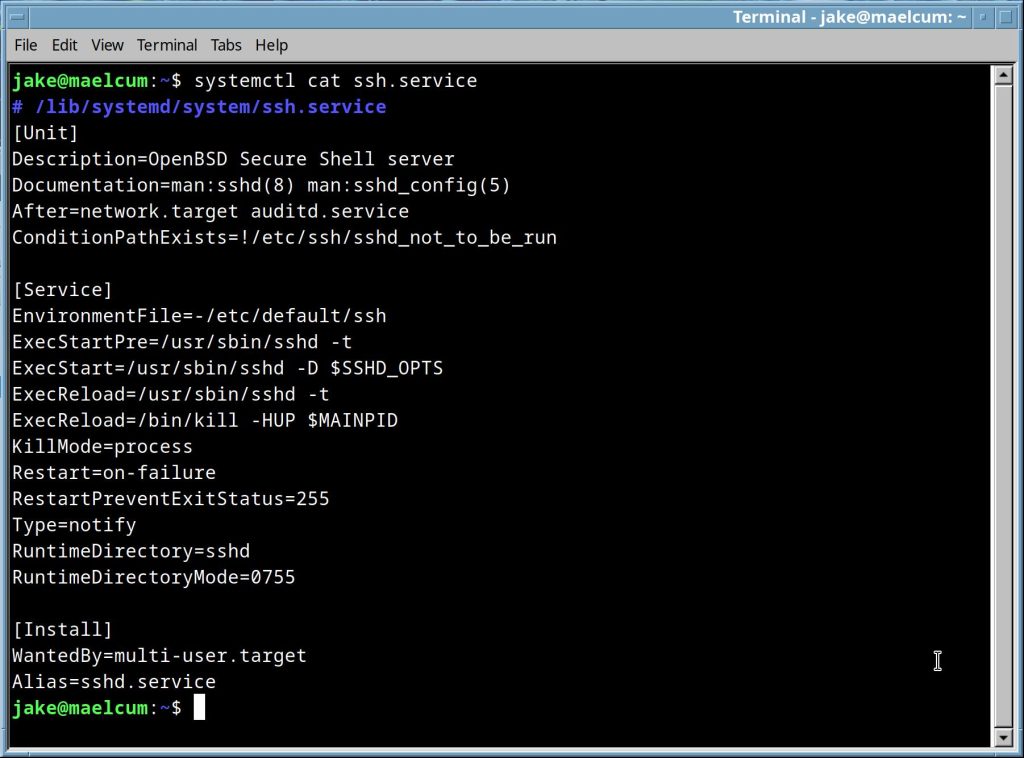 |
systemctl list-dependencies <application>.service |
Will list all the services this service is dependent upon for proper operation, recursively, in a nice tree. it’s output can be quite long, so i am not going to post a screenshot. The –reverse flag will show services that depend on the specified service. |
File and Disk Management
| Command | Description | |
mdadm |
I have a full walkthrough here | |
cp <options> <file or folder 1> <file or folder 2> |
copies files. wanna copy a directory? cp -r, this copies everything recursively. | |
rm <options> <file or folder name> |
|
|
tar -czvf <archivename.tar> <Path to folder> |
This tars up with zip compression the target folder. it’s good for backing up whole partitions. | |
tar -xzvfp -C <path to destination folder> |
extracts and unzips everything into the destination folder. | |
tar -tvf <archivename.tar> |
lists a tar files contents | |
dd if=<ISO filename> of=/dev/<disk> bs=4M status=progress |
writes an ISO file to a disk. ANY disk. dd is powerful and dangerous. make sure <disk> is the correct (USB) disk before hitting that enter key. |
|
dd if=/dev/<disk1> of=/dev/<disk2> bs=4M status=progress |
clones <disk1> onto <disk2>. it will happily and quickly destroy any existing data on <disk2>, with no regards to your feelings. |
|
dd if=/dev/<disk> of=<backup file> bs=4M status=progress |
creates an image of <disk> and stores it in <backup file>. this is a handy way to backup smaller disks, but AFAIK it does no compression, so each backup is the size of the original filesystem. |
|
dd if=<backup file> of=/dev/<disk> bs=4M status=progress |
Restores the aforementioned backup. | |
dd if=/dev/urandom of=/dev/<disk> bs=4M status=progress |
Securely and irrevocably wipes a drive. |